Tracking Embodied Carbon in Buildings
Understanding embodied carbon in assets throughout the whole life of a building is critical for the clients we work with keen to reduce emissions. Building services consultancy engineers have always been focused on improving the design and efficiency of a building to optimise its performance and now more than ever, sustainability runs through every single part of our services. An integral part of the sustainability service we offer to our clients is producing embodied carbon reports.
What is embodied carbon?
Embodied carbon is the calculation of carbon emissions associated with materials and construction throughout the whole life cycle of a building or infrastructure. This encompasses any process concerning the asset such as maintenance, refurbishment, repairs, and repurposing buildings.
Buildings are increasingly utilising electricity generated through green and sustainable energy sources which has had a positive impact on building emissions. The focus now for sustainable engineering consultancy is on carbon produced through manufacturing, maintenance and end of life scenarios of buildings.
The challenge comes in anticipating which services or parts of a building will need to be replaced and how often over the lifespan of a building. Skilled engineers such as the sustainability team at Cudd Bentley must consider the impact in real terms of whole-life carbon impact. We find it helpful for our clients to visually show them how this standard consists of modules and break stages based on the definitions of BS EN 15978:2011.
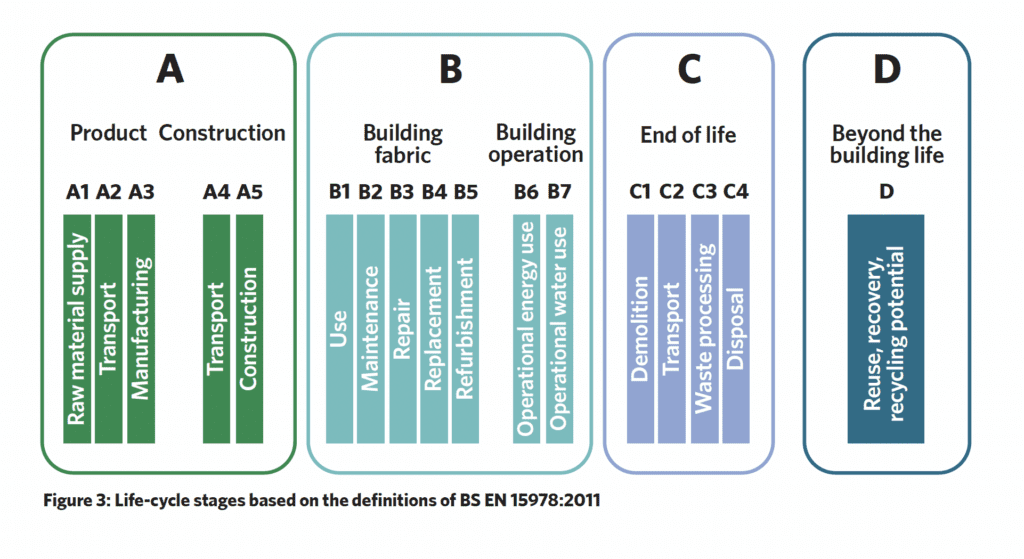
Product & construction:
The first set of system boundaries defined by EN BS 1598:2011, A1 to A3 – also known as cradle to gate – are focused on the carbon that is released through raw material extraction, the manufacture of components and building elements as well as the transportation of materials throughout this process, up to the point the product is ready to leave the factory. Modules, A4 to A5 covers the transportation of construction products and all construction processes, including wastage, up to project completion.
Building fabric and operation
Modules B1 to B7 cover the building in its usage stage. This encompasses carbon emissions related to daily use as well as operational energy, maintenance, and repairs.
End of life
There are emissions which are released when a building is decommissioned and modules C1 to C4 deal with this. At this stage emissions will be measured around demolition, transporting of waste materials from the site as well as their disposal.
Beyond the building life
This final stage addresses how elements of the building may be reused and the potential for recycling or recovering any parts of the building; this is offset against the carbon emissions.
Whilst it is a complex and involved process, measuring embodied carbon from assets, using a methodology as stipulated by BS EN 15978:2011 gives sustainability teams, a clear framework that helps our clients in multiple sectors, make decisions around their buildings. Utilising this framework and its boundaries means that clients have visibility on which areas have the greatest potential to produce emissions and where needed, adjust, and make choices armed with that knowledge.


